Simultaneous use of escitalopram and Viagra requires careful consideration. Consult your doctor before combining these medications. This isn’t a simple yes or no answer, as individual responses vary greatly.
Viagra (sildenafil) affects blood flow, while escitalopram (Lexapro), an SSRI antidepressant, can subtly influence neurotransmitter systems potentially affecting blood pressure regulation. The interaction isn’t always significant, but it’s prudent to monitor for any unexpected side effects, particularly hypotension (low blood pressure) or dizziness. Your physician can assess your specific health status and determine if combining these medications is safe for you.
Key factors your doctor will consider include: your overall health, existing medical conditions, other medications you’re taking, and your response to individual treatment. Open communication with your healthcare provider is vital. Regular check-ups allow for timely adjustments to your treatment plan as needed. Never adjust dosages or stop taking any medication without your doctor’s explicit instructions.
Remember, this information serves as a general guideline. It does not replace the advice of a qualified medical professional. Always seek personalized medical advice for your specific situation. Your doctor can provide specific recommendations based on your individual needs and health history.
- Escitalopram and Viagra: Understanding Potential Interactions
- Escitalopram: A Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI)
- Viagra (Sildenafil): Mechanism of Action and Indications
- Pharmacokinetic Interactions: Absorption, Metabolism, and Elimination
- CYP Enzyme Interactions
- Absorption and Elimination
- Potential for Increased or Decreased Efficacy of Viagra
- Factors Influencing Efficacy
- Alternative Approaches
- Side Effects and Increased Risk with Combined Use
- Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Concurrent Use
- Specific Risks and Precautions
- Recommendations
- Alternative Treatments
- Importance of Physician Consultation Before Combined Use
- Understanding Potential Risks
- Personalized Medication Management
- Patient-Specific Considerations and Monitoring
- Cardiac Monitoring
- Dosage Adjustments
Escitalopram and Viagra: Understanding Potential Interactions
Consult your doctor before combining escitalopram and Viagra. This is crucial due to potential interactions.
Viagra (sildenafil) increases blood flow, and escitalopram, an SSRI antidepressant, can affect blood pressure. This combination might lower blood pressure excessively, potentially causing dizziness or fainting. The severity depends on individual factors like dosage and overall health.
Specific interactions aren’t fully understood, and research is ongoing. However, a significant risk of hypotension exists. Your doctor needs to weigh the benefits of both medications against these risks.
Be aware of potential side effects such as headaches, nausea, or flushing. Report any unusual symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider.
They might adjust dosages or suggest alternative treatments based on your health profile and needs. Open communication with your physician is key to managing this combination safely.
Never alter your medication regimen without your doctor’s approval. This includes adjusting dosages or stopping treatment prematurely.
Escitalopram: A Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI)
Escitalopram belongs to a class of medications called Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors, or SSRIs. It primarily works by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that plays a significant role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and other bodily functions. Low serotonin levels are often associated with depression and anxiety disorders.
- Escitalopram helps alleviate these symptoms by preventing the reabsorption of serotonin, allowing it to remain active in the synapses longer.
- This leads to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Prescribing information varies, but common dosage ranges from 5mg to 20mg daily. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and response to treatment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Like all medications, Escitalopram can have side effects. These can include:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Insomnia
- Sexual dysfunction
Most side effects are mild and temporary. However, serious side effects are rare but possible. Consult your physician immediately if you experience unusual symptoms.
Remember, Escitalopram is a prescription medication. Never start or stop taking it without your doctor’s guidance. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
- Discuss any concerns or questions you have about Escitalopram with your doctor or pharmacist.
- Inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Do not drink alcohol excessively while taking Escitalopram.
Viagra (Sildenafil): Mechanism of Action and Indications
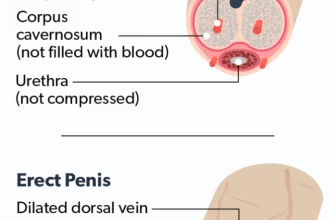
Sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra, works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This enzyme breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a crucial molecule for achieving and maintaining an erection. By blocking PDE5, sildenafil allows cGMP levels to rise, resulting in increased blood flow to the penis.
This increased blood flow is necessary for a firm erection. The process begins with sexual stimulation, triggering the release of nitric oxide, which in turn increases cGMP. Sildenafil enhances this natural process.
Viagra is primarily indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) in adult men. It helps men achieve and maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse. It’s important to note that Viagra does not directly cause an erection; sexual stimulation is still required.
| Indication | Details |
|---|---|
| Erectile Dysfunction (ED) | Improves ability to achieve and maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. |
| Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) | Under a different brand name, sildenafil is also used to treat PAH, a serious condition affecting blood vessels in the lungs. This is a separate indication and requires a different dosage and prescription. |
Always consult a healthcare professional before taking Viagra or any medication. They can assess your individual health status and determine the appropriate dosage and suitability of the medication for you. Discuss potential side effects and interactions with other medications you may be taking.
Pharmacokinetic Interactions: Absorption, Metabolism, and Elimination
Escitalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), and sildenafil (Viagra), a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, don’t directly compete for the same metabolic pathways. However, both medications are extensively metabolized by the liver, primarily via the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system. Specifically, escitalopram is mainly metabolized by CYP2C19, while sildenafil is metabolized by CYP3A4.
CYP Enzyme Interactions
Although primary metabolic pathways differ, concurrent use might still lead to subtle interactions. CYP2C19 inhibition could slightly increase escitalopram levels. Conversely, CYP3A4 induction might marginally reduce sildenafil’s efficacy. These effects are usually minimal for most individuals, but those with impaired hepatic function may experience more pronounced changes. Consult your physician if you have liver disease.
Absorption and Elimination
Escitalopram’s absorption is not significantly affected by sildenafil. Both drugs are well-absorbed orally. Elimination occurs primarily through hepatic metabolism and renal excretion. The impact on elimination kinetics is generally mild, but individual variation exists. Regular monitoring by your doctor is advised, especially in individuals with renal impairment, to optimize dosage and prevent potential adverse effects.
Potential for Increased or Decreased Efficacy of Viagra
Currently, there’s limited direct research exploring the combined effects of escitalopram and Viagra. However, we can consider potential interactions based on their known mechanisms. Escitalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), affects serotonin levels in the brain. Viagra, or sildenafil, increases blood flow to the penis. Some studies suggest SSRIs might slightly delay or reduce the effectiveness of Viagra, potentially by impacting nitric oxide pathways involved in penile erection. This effect isn’t consistently observed, and individual responses vary greatly.
Factors Influencing Efficacy
Several factors influence the interaction: dosage of both medications, individual patient factors (e.g., age, overall health, other medications), and the severity of erectile dysfunction. Higher escitalopram doses might be associated with a greater chance of reduced Viagra effectiveness. Always discuss any medication interactions with your doctor before combining them. Open communication with your physician is crucial for safe and effective treatment. Your doctor can adjust dosages or recommend alternative treatments to optimize your results and minimize potential side effects.
Alternative Approaches
If you experience reduced Viagra efficacy while taking escitalopram, your doctor may suggest alternative treatments for erectile dysfunction, such as phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors with different profiles or other approaches. They can help you weigh the potential benefits and risks of various treatment options based on your specific situation. Remember that open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount.
Side Effects and Increased Risk with Combined Use
Combining escitalopram and Viagra can increase the risk of several side effects. Priapism, a persistent and painful erection lasting more than four hours, is a serious concern. Seek immediate medical attention if this occurs.
You might experience an increased likelihood of nausea, dizziness, and headaches. Low blood pressure, leading to fainting or lightheadedness, is also possible. Some individuals report increased sleepiness or fatigue.
Be aware that escitalopram can reduce libido; Viagra’s effect on this may be counteracted. Discuss any changes in sexual function with your doctor.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking before starting any new treatment. This allows for a careful assessment of potential interactions and helps minimize risks.
Closely monitor yourself for any unusual side effects. Report any concerns to your physician promptly to ensure you receive the appropriate care and management.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance based on your individual health status and medical history.
Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Concurrent Use
Combining escitalopram and Viagra (sildenafil) may increase your risk of cardiovascular events. This is because both medications can affect blood pressure and heart rate. Escitalopram, an SSRI antidepressant, can sometimes lower blood pressure. Sildenafil, used to treat erectile dysfunction, lowers blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels. This combined effect can lead to hypotension (low blood pressure) – especially dangerous in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
Specific Risks and Precautions
- Hypotension: A significant drop in blood pressure can cause dizziness, fainting, and even more serious complications.
- Bradycardia: A slow heart rate can occur, particularly in individuals sensitive to either medication.
- Syncope (fainting): The combined effect of lowered blood pressure and heart rate significantly increases the risk of fainting.
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack): While not directly caused by the combination, the added strain on the cardiovascular system increases the risk, particularly in patients with pre-existing heart disease.
Before starting concurrent use, a thorough cardiovascular assessment is recommended.
Recommendations
- Consult your doctor: Discuss your medical history, including any heart conditions, and current medications with your physician before starting either escitalopram or Viagra, especially if you plan to take them together.
- Start with low doses: Your doctor might prescribe lower doses of either medication to minimize the risk of side effects.
- Monitor for side effects: Pay close attention to any symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, chest pain, or irregular heartbeat, and contact your doctor immediately if these occur.
- Regular check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor your cardiovascular health while taking both medications.
Alternative Treatments
If you’re experiencing erectile dysfunction, your doctor might explore alternative treatments that don’t carry the same cardiovascular risks as sildenafil, when used with escitalopram. These alternatives could include lifestyle changes, other medications, or even psychological therapies.
Importance of Physician Consultation Before Combined Use
Always consult your doctor before combining escitalopram and Viagra. This is crucial because both medications affect blood pressure and can interact in unpredictable ways. Viagra increases blood flow, while escitalopram can sometimes lower blood pressure. This combination may lead to dizziness, fainting, or even more serious cardiovascular events.
Understanding Potential Risks
Some men taking escitalopram experience side effects like low blood pressure or fainting. Combining this with Viagra, which further lowers blood pressure, significantly increases the risk of these side effects. Your physician can assess your individual risk factors, such as pre-existing heart conditions or other medications you’re taking, to determine the safety of this combination. They can also recommend alternative treatments if necessary.
Personalized Medication Management
Your doctor will consider your medical history and current health status to create a safe and effective treatment plan. They might adjust dosages, suggest alternative medications, or monitor you closely for any adverse reactions. Open communication with your doctor is paramount to ensure your safety and well-being.
Patient-Specific Considerations and Monitoring
Regularly monitor blood pressure, especially during initial treatment. Escitalopram can sometimes lower blood pressure, and this effect may be enhanced by Viagra. Report any dizziness or fainting spells to your doctor immediately.
Cardiac Monitoring
Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions require close cardiac monitoring. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) may be necessary, particularly if you experience chest pain or palpitations. Discuss any heart concerns with your physician before starting either medication.
Dosage Adjustments
Your doctor may adjust the dosage of either escitalopram or Viagra, or both, based on your response and potential side effects. Open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount for optimal management.
Be aware of potential interactions with other medications. Always inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This allows for a safer and more effective treatment plan.
Monitor for serotonin syndrome symptoms, including agitation, confusion, rapid heart rate, and high fever. Seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms appear. This is particularly important in the initial stages of treatment.
Regularly review your treatment plan with your doctor. This ensures that the medication regimen remains appropriate and addresses any changes in your health status.